CBDA for Pain – The Science
Are you experiencing joint pain that’s disrupting your daily routine? Maybe you’re facing the relentless throbbing of endometriosis or noticing stiffness creeping into your joints, making movement a challenge. If any of these scenarios resonate with you, it’s time to seek relief.
Pain is caused by many different underlying conditions, and prevents you from enjoying the activities and social events that make life so enjoyable. Finding the right pain relief can be difficult, as many solutions offer minimal relief and concerning side effects.
Pain relief is a routine, and finding support in the right routines is critical to getting back to your normal self. Below, we’ll introduce the concept of CBDA for pain relief so you can try nature’s goodness as a treatment method. You’ll not only learn the connection between CBDA and pain, but also how to use it and where to find high-quality CBDA for sale – right here at Natural Dos!
What is pain?
Pain comes in many forms, but fundamentally, it is a neurological signal to the brain that something is wrong in the body. We all know the feeling. But, let’s dive a bit deeper to understand what’s going on in your body.
Chronic pain is often a result of chronic inflammation that leads to temporary, and sometimes permanent damage if not treated appropriately. Often, dealing with the inflammation directly, as well as what is causing the inflammation can improve symptoms.
Fundamentally, inflammation evolved as a mechanism to prevent infection from external pathogens. In modern society, inflammation is mostly a cause of chronic pain and disease, thus many anti-inflammatory drugs and treatments to decrease its long-term harmful effects.
While this topic is extensive and is the subject of a lot of research, the connection between inflammation and pain is widely accepted in the medical community.
What is CBDA?
So, what is CBDA? The cannabis plant, which includes hemp and marijuana, has over 100 different cannabinoids. While each cannabinoid is structurally different, they all have some common properties that involve interacting with the endocannabinoid system.
Most of the cannabinoids are located in the flower, but there are minor amounts also found in the stem. The cannabinoids in the cannabis plant are naturally in the acidic form. Below is a partial list of the different acidic cannabinoids:
- CBDA (cannabidiolic acid) & CBD (cannabidiol)
- THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) & THC (tetrahydrocannabinol)
- CBGA (cannabigerolic acid) & CBG (cannabigerol)
- CBCA (cannabichromenic acid) & CBC (cannabichromene)
- CBDVA (cannabidivarinic acid) & CBDV (cannabidivarin)
- THCVA (tetrahydrocannabivarinic acid) & THCV (tetrahydrocannabivarin)
- CBNA (cannabinolic acid) & CBN (cannabinol)
What the Science Says About CBDA for Pain Relief
Cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) is not as well studied as CBD and THC since its isolation methods are more difficult and is only recently gaining in popularity.
That being said, many people are reporting significant benefits from taking CBDA, and may represent the new cannabis plant medicine in the space. Most of the research on CBDA has been performed by in vitro (cell culture) and in vivo (animal) studies.
COX2, CBDA and inflammation
There is a direct link between CBDA and inflammation. The cyclooxygenase (COX) class of enzymes is critical to many inflammatory processes. These enzymes produce prostaglandins which enhance the pro-inflammatory mechanisms in many cells. One of the major COX enzymes is COX 2, which is well noted for its role in promoting many inflammatory states during injury, cardiovascular disease, joint swelling, cancer, and many other pathologies.
Why is COX2 important? The NSAID (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory) drug class is commonly used for pain relief. These drugs, such as ibuprofen and aspirin, target the COX2 enzyme form to reduce inflammation and pain.
Some of the first studies with CBDA found that it can inhibit the activity of COX2. In this study using breast cancer cells, CBDA inhibited COX 2 activity.
In addition to direct inhibition, other studies in breast cancer cells found that it also affects the expression of COX2. Breast cancer cells exposed to CBDA lowered the expression of COX 2, meaning that there was less enzyme present.
NSAIDS, such as celecoxib, have been used in treatment for breast cancer, and have been associated with reduced incidence.
This data suggests that CBDA may be important in the treatment of inflammation and pain relief.
CBDA and pain relief
In this study out of Canada, using an animal model of inflammatory pain management, CBDA, and THC both alone and together were tested. Administration of CBDA was found to have anti-inflammatory and pain relief properties.
This in vivo study suggests that CBDA pain management is through the transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1 antagonist (TRPV1). This was determined by using an inhibitor, and then treatment with CBDA, which prevented the effects of CBDA.
TRPV1 is associated with the endocannabinoid system and is also a target of capsaicin, the compound known for inducing the hot feeling in spices from peppers. Interestingly, there is considerable research into using capsaicin for its pain management properties.
CBDA vs CBD for Pain
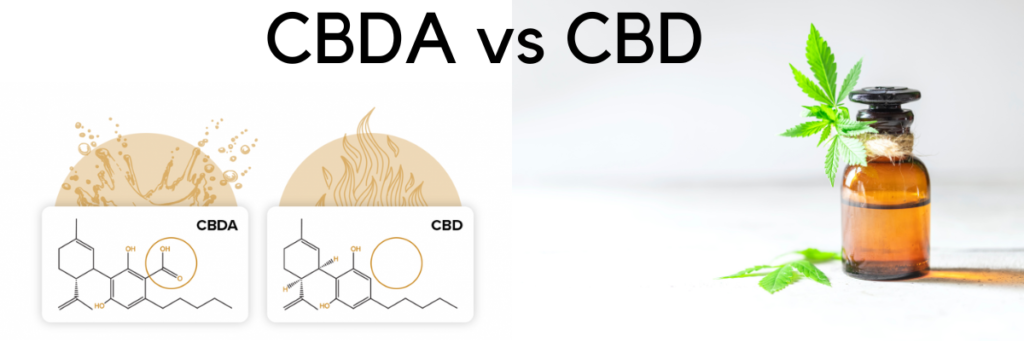
So much of the conversation on using cannabis for pain relief is centered on CBD – but as we discuss in our comparison of CBDA vs CBD, there’s reason to rely on the acidic cannabinoid over its more popular decarboxylated form.
CBDA is the mother compound to CBD, and is naturally found in the hemp flower in large concentrations depending on the strain. CBD oil is derived from CBDA after it has been exposed to significant heat.
The raw form of cannabis plant extract contains mostly acidic cannabinoids depending on how well it is stored.
The conversion is termed CBDA decarboxylation and is found during conventional purification processes of extracted hemp oil. Typically, the first extraction of the hemp flower produces a low-quality crude extract that requires further purification of the cannabinoids.
The benefits of CBDA and CBD oil have been studied for their potential medical benefits, and while there is some therapeutic overlap there are some significant differences.
CBDA does not need to be decarboxylated to be active
CBDA has its own properties that make it unique and different from CBD, and may have better therapeutic potential because it is not decarboxylated. This notion that a cannabinoid needs to be heated before it is active came from the marijuana field, where THCA gives less of a high than THC due to the difference in CB1 receptor activation.
Endocannabinoid system
Cannabinoids are known for their interaction with the endocannabinoid system (ECS). The ECS is found throughout the body, and with strong expression in the brain and immune system.
The ECS helps regulate many physiological processes, such as mood, sleep, inflammation, and blood pressure. While all cannabinoids interact with the ECS in some fashion, there are significant differences in how they do and what their effects are.
For example, THC is known to have psychoactive properties that confer the euphoric feeling people associate with marijuana. However, CBDA and CBD are not considered psychoactive and do not get you high.
These different effects are typically through the cannabinoid receptors, such as cannabinoid receptors 1 and 2 (CB1, CB2). THC may activate CB1, which elicits it euphoric feeling, whereas CBD is an allosteric inhibitor of CB2.
CBDA is known to help activate CB2, but also has other effects on different endocannabinoid receptors, such as the 5HT1A receptor. This receptor is associated with serotonin recycling in the brain, and is also a target for depression drugs in the SSRI (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor) class.
CBDA has enhanced absorption
A significant difference between acidic cannabinoids like cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), is that they have much better absorption than decarboxylated cannabinoids like CBD. Multiple studies have tested the absorption levels of acidic and decarboxylated cannabinoids by ingestion to see how much is taken up by the body.
How well the body absorbs a compound is critical to how effective compounds are at exerting any potential therapeutic effects. This is why the increased CBDA absorption rates are so profound.
A recent study out of the University of Sydney found that CBDA is absorbed over 100 times better than CBD. This seems incredible, but their results were significant and follow a similar trend seen in other CBDA absorption studies.
Further, this University of Sydney study showed that CBDA absorption was enhanced by the presence of other cannabinoids, highlighting the importance of having all the cannabinoids present in a dose.
This means that reaching potent therapeutic doses of CBDA may require only low doses to be ingested. So, why is it so hard to find high-quality CBDA products?
Why do I not see more CBDA on the market?
Conventional processing requires the use of heat to purify the cannabinoids from crude extract after hemp flower harvesting. This has led to widespread use and marketing of CBD and CBG as the standard cannabinoid products.
Scientists at Natural Dos developed a new technology to isolate only the acidic cannabinoids without adding heat. This has allowed us to preserve the natural therapeutic properties of acidic cannabinoids in all our products.
We’ll introduce you to the best CBDA tincture and other world-class products you can use for pain relief below.
How to Use CBDA for Pain Relief
Now that you’re up to speed on how CBDA can support your body in the path to pain-free living, how do you actually go about using it? We’ll talk you through choosing the right products and incorporating them into your regimen below.
Finding Quality CBDA Products
When considering CBDA for pain relief, the first step is to ensure you are selecting high-quality products. Look for items that have been third-party lab tested, which verifies the product’s purity, potency, and absence of harmful contaminants.
Reputable manufacturers will often provide Certificates of Analysis (COAs) for their products. Opt for CBDA products sourced from organically grown hemp and extracted using methods that preserve the integrity of the cannabinoids.
If you’re interested in seeing how this obscure little cannabinoid can provide relief in your own life, you’re in the right place. Natural Dos is pioneering the CBDA landscape with potent, pure products that have helped thousands of individuals around the world.
We use an innovative extraction method that preserves as much CBDA as possible, and you can rest assured you’re getting the quality you deserve through our transparent policies.
Plus, we have everything from the best CBDA oil to edibles, empowering you to find a delivery method that aligns with your lifestyle and preferences. Here are our most popular categories:
You can place your order with peace of mind knowing it’s backed by our 100-day, 100% satisfaction guarantee. So, take a look at what we have to offer and give your body the support it needs to put problems with pain in the past.
Ideal Dosage for Pain
Determining the ideal dosage of CBDA for pain relief can be challenging as it varies from person to person. Start with a low dose and gradually increase it until you find relief. Your goal is to find the minimum effective dose (known as MED), and stick to that. You can titrate (slowly increase your dose) until you find relief.
For most people, a dose of 10mg to 100mg per day is ideal. Still, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider familiar with cannabinoids to help guide your dosage, especially if you are taking other medications.
Timing and Lifestyle Integration
Consistent use of CBDA may be necessary to manage chronic pain effectively. Incorporate CBDA into your daily routine, taking it at regular intervals to maintain a consistent level in your system.
Some individuals find relief by using CBDA alongside other pain management techniques, such as physical therapy or in conjunction with other natural supplements. That being said, here are a few other tips on managing pain below.
Other Tips on Managing Pain
In addition to using CBDA to manage pain, consider incorporating these strategies into your pain management plan:
- Exercise: Engage in low-impact activities like swimming, cycling, or yoga to increase blood flow and reduce inflammation.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Apply heat to relax muscles and improve circulation or use cold to reduce inflammation and numb sore areas.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Practice deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, or guided imagery to reduce stress and pain perception.
- Dietary Adjustments: Anti-inflammatory foods, such as omega-3 rich fish, leafy greens, and berries, may help manage pain naturally.
- Adequate Sleep: Ensure you get quality sleep, as lack of rest can exacerbate pain.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water, as dehydration can worsen pain symptoms.
Remember, while CBDA holds promise for pain relief it’s important to get a healthcare professional’s advise to at least rule out more serious complications or conditions that could be causing pain.
Nevertheless, this potent little cannabinoid has great potential to relieve chronic pain, whether you’re dealing with back pain or recovering from surgery. So, shop at Natural Dos today and feel the difference it can make in your life firsthand!
Parting Thoughts on Using CBDA for Pain
There you have it – everything you need ot know about CBDA for pain. Inflammation is typically considered a significant underlying contribution to pain and is a common target for many over-the-counter pain management drugs. Many patients are prescribed potent pain medications, such as opioids, which can have significant complications.
Cannabis plant raw-form extracts that contain high amounts of CBDA may provide an alternative to traditional therapeutics, but more research is needed.
The FDA has not approved CBDA or other cannabinoids for pain management, so please consult with your healthcare provider if you are currently on medication. Since CBD in high doses has been found to have some drug-drug interactions, it’s important to seek advice from your physician if you are on multiple medications.
Our blog has more resources on the CBDA benefits, including using CBDA for sleep, CBDA for nausea, CBDA for depression, CBDA for anxiety, CBDA side effects, CBDA vs CBDV, CBDA vs CBG, and more.
But at this point, it’s time you invested in your health and wellbeing by shopping at Natural Dos to discover firsthand how CBDA can ease your suffering. With our 100-day money-back guarantee, what do you have to lose? Put pain in the past by harnessing the power of CBDA today.






